

What is Retina?
The retina is the light-sensitive layer of tissue that lines the inside of the eye and sends visual messages through the optic nerve to the brain. The central part of the retina is called macula
which is responsible for fine detailed
central vision.

What is Retinal Detachment?
Retinal Detachment (RD) occurs when retina separates from its underlying layers which provide nutritional support to the retina. If not promptly treated, retinal detachment can
cause permanent and even complete vision loss.
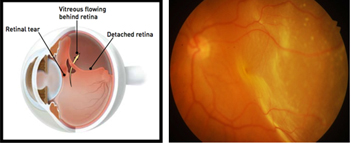
How does retinal detachment occur?
RD may be caused due to tears or holes in the retina (Rhegmatogenous RD), traction on the retina (Tractional RD) or if fluid is built up under the retina (Exudative RD)
What are the risk factors for retinal detachment?
A retinal detachment is also more likely to occur in people who have:
What are the symptoms of retinal detachment?

What are floaters and flashes of light?
Floaters are small, dark, shadowy shapes that can look like spots, thread-like strands, cob webs or squiggly lines that move in your field of vision. Flashes look
like flashing lights or lightning streaks in the peripheral vision even though no light is actually flashing. Floaters are very common and is usually not a sign of a serious condition. However, if floaters and/or flashes
begin or increase suddenly, it may indicate a serious problem, and hence needs immediate medical attention.
What is the treatment of retinal detachment?
RD can be treated in any of the following ways:
Pneumatic retinopexy involves injection of a gas bubble into the vitreous (the jelly-like substance in the eye cavity) enabling the gas bubble to push the retinal tear back against the wall of the eye and
close the tear. Laser or cryopexy (freezing) is used to secure the retina to the eye wall around the retinal tear. .

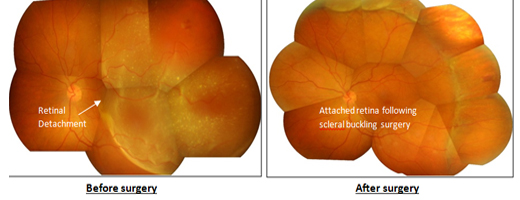
Scleral buckle surgery involves suturing a silicone “buckle” to the eye that indents the wall of the eye to support the retinal breaks allowing the retina to reattach.Cryopexy (freezing) treatment is usually
used to seal the retinal tears.
The silicone buckle is usually left on the eye permanently. Someone looking at you cannot see the buckle, as it is stitched to the sclera somewhere towards the back of the eye.
At Kumta Eye and Retina clinic, we perform highly specialized minimally invasive buckling technique called Minimal Scleral Buckling.

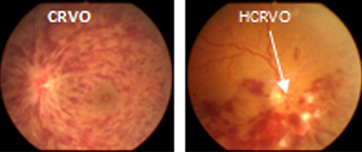
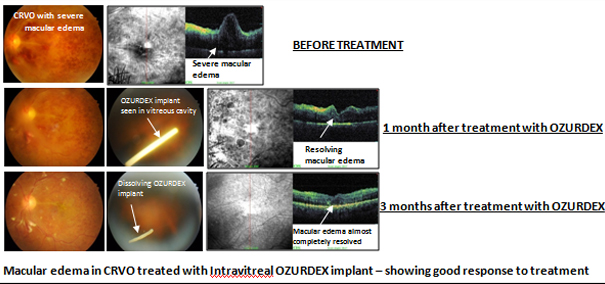
Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) –occurs when the main (central) retinal vein gets blocked, thus leading to involvement of the entire retina. Less commonly, Hemi central retinal vein occlusion (HCRVO) may occur when there is blockage of a vein draining the superior or inferior half of the retina.
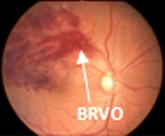
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO)occurs when there is a blockage within a branch of the retinal vein leading to hemorrhage along the distribution of a small vessel of the retina.
What are the types of CRVO?
Non ischemic CRVO – it is a is a milder form of the disease where the blood supply of the retina is not affected Ischemic CRVO – it is a more serious form where the blood supply
of the retina is lost, hence can lead to the development of significant complications,vision loss and rarely loss of eye.
What are the symptoms of RVO?
Patient with RVO may complain of sudden painless loss of vision in the affected eye. There may be minimal or no symptoms if macula is not affected.
What are the risk factors for RVOs?
High blood pressure, Diabetes, High cholesterol, elevatedHomocysteine levels, Ocular hypertension & Glaucoma, Fasting especially water deprivation
What is the treatment for RVO?
There is no treatment proven to reopen occluded retinal veins. Strict control of all risk factors is very important.
Intravitreal Anti-VEGF injections ( Lucentis /Avastin)–to reduce macular edema and improve vision. It may sometimes be combined with a steroid injection.
Intravitreal steroid injections (Triamcilnolone/ Ozurdex implant) – to reduce macular edema and improve vision. Can be combined with Anti VEGF injections.
Laser Photocoagulation-Laser treatment is applied to whole peripheral retina (PRP in ischemic CRVO) or affected retinal area in BRVO to decrease the risk of further complications. Laser does not improve
sight.
Vitrectomy – May be required in cases of non resolving vitreous haemorrhage due to RVO.
What is Age related macular degeneration (AMD)?
AMD is a disease that is associated with aging that gradually destroys the macula thus affecting central vision in the affected eye.
What are the types of AMD?
AMD occurs in two forms:

Dry AMD -Occurs when the light sensitive cells in the macula slowly break down gradually blurring central vision.
Wet AMD - Occurs when new abnormal blood vessels which are very fragile start growing beneath the macula which may often leak blood and/or fluid causing rapid loss of central vision.
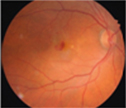
What are the Symptoms of AMD?
Blurred central vision, distorted vision, difficulty in recognizing faces and reading

What is the treatment for AMD?
There are two main treatment options for wet AMD:
Non proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR)– is an early form of the disease where patient may usually not have any vision complaints. It is classified as mild, moderate and severe NPDR depending on the amount of retinal damage.

Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) – is a more advanced form of the disease where new abnormal blood vessels grow on retinal surface (in response to the loss of blood supply caused by closure of normal blood vessels) which can bleed anytime (vitreous haemorrhage) or cause pull on the retina (tractional retinal detachment) leading to sudden loss of vision. Neovascular glaucoma (NVG) may occur in end stages which may lead to a painful blind eye.
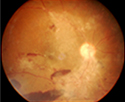
What is Diabetic macular edema (DME)?
DME is swelling or thickening of the macula due to fluid leakage from damaged blood vessels within the macula due to diabetes causing blurring of vision. DME can occur
at any stage of DR.
How is Diabetic Retinopathytreated?
In the early stages of NPDR, treatment other than regular monitoring is not required. Strict control of diabetes, blood pressure and cholesterol is very important
to control progression of DR.
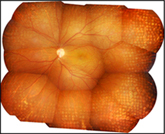



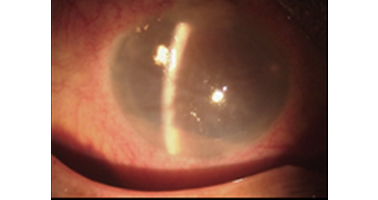

What are the symptoms of Vitreoretinal diseases?
Since this is a macular disease, central vision is mainly affected - blurred central vision with difficulty reading and recognizing faces, distorted vision,
gray spot in central vision (central scotoma)
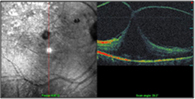

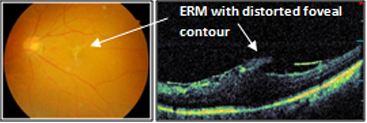
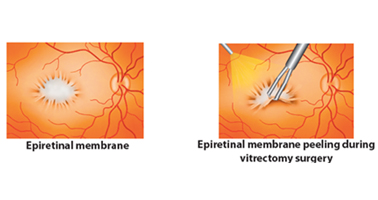

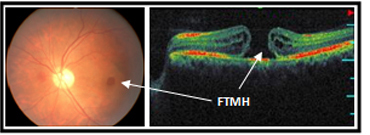
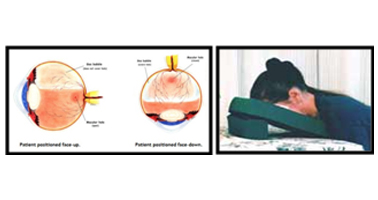
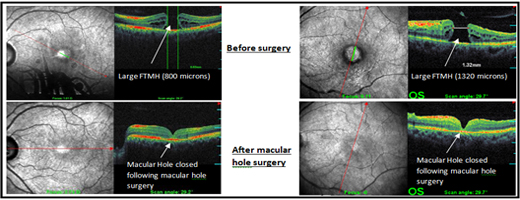
The other retinal conditions treated at Kumta Eye & Retina Clinic are
Retinopathy Of Prematurity (ROP), Ocular trauma & Management of cataract surgery complications like dislocated nucleus, dislocated Intraocular lens (IOL), and endophthalmlitis.


Spectral Optical coherence tomography (3D OCT/SLO) from OPKO (USA)

Multispot Pattern Laserfrom Iridex (USA)
Laser treatment involves using an intense beam of light (laser) that can be precisely focused on the retinal areas to be treated.
It is widely used for treatment
of Diabetic retinopathy and other retinal vascular disorders. It is also used to seal retinal tears or holes in patients as preventive treatment of retinal detachment.
As compared to conventional laser, multispot laser
is extremely fast, require shorter sessions, causes less damage to surrounding tissues hence lesser visual defects and causes less pain hence well tolerated by patients,br> 

Advanced Vitreo-Retinal Surgical Facilities with Constellation combined vitrectomy system from Alcon (USA), Leica M501 zoom operating microscope with XY & Camera (Swiss), BIOM & sutureless MIVS (Microincisional Vitrectomy Surgery) technology

Sutureless vitrectomy
What isMicroincisional Vitrectomy Surgery(MIVS)?
Vitrectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removal of vitreous gel from the eye by making incisions in the sclera (the white part of our eye) to gain access into the vitreous cavity and the retina. In conventional vitrectomy,these
incisions are relatively large and sutures are required to close these incisions.
In Microincisional Vitrectomy Surgery,the incisionis made with specialized instruments and is much smaller than in conventional vitrectomy, and
therefore they close by themselves and donot require sutures.MIVS is done with a specialized vitrectomy system called Constellation.There are 3 techniques available in MIVS: 23 Gauge, 25 Gauge and 27 Gauge Vitrectomy
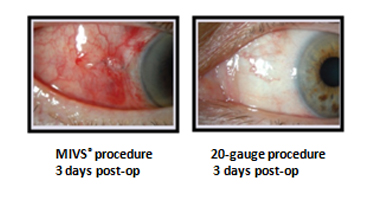
What are the advantages of MIVS?
Since it is sutureless, foreignbody sensation related to sutures is not there. Since size of the incisions in MIVS is very tiny, healing time is much faster and postoperative
discomfort, pain, and redness is minimal as compared to conventional vitrectomy.



Photodynamic therapy (PDT)with Visudyne
PDT uses a light sensitive dye – Visudyne which when injected, accumulates in abnormal blood vessels in the eye and a cold laser is used to activate the drug which then
seals the abnormal vessels without damaging the overlying sensory retina. It is used in treatment of wet age related macular degeneration, Chronic Central serous retinopathy